Note
Click here to download the full example code
Calculating and plotting the relative vorticity¶
Vorticity, the microscopic measure of rotation in a fluid, is a vector field defined as the curl of velocity (James R. Holton, Gregory J. Hakim, An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, 2013, Elsevier : Academic Press p95-125). In this recipe, we will be calculating and plotting the relative vorticity from the wind components.
Import cf-python and cf-plot:
import cfplot as cfp
import cf
Read the field constructs:
[<CF Field: divergence_of_wind(long_name=time(3), long_name=expver(2), long_name=latitude(721), long_name=longitude(1440)) s**-1>,
<CF Field: eastward_wind(long_name=time(3), long_name=expver(2), long_name=latitude(721), long_name=longitude(1440)) m s**-1>,
<CF Field: northward_wind(long_name=time(3), long_name=expver(2), long_name=latitude(721), long_name=longitude(1440)) m s**-1>]
Select wind components and look at their contents:
u = f.select_field("eastward_wind")
print(u)
Field: eastward_wind (ncvar%u)
------------------------------
Data : eastward_wind(long_name=time(3), long_name=expver(2), long_name=latitude(721), long_name=longitude(1440)) m s**-1
Dimension coords: long_name=time(3) = [2023-01-01 00:00:00, 2023-02-01 00:00:00, 2023-03-01 00:00:00] gregorian
: long_name=expver(2) = [1, 5]
: long_name=latitude(721) = [90.0, ..., -90.0] degrees_north
: long_name=longitude(1440) = [0.0, ..., 359.75] degrees_east
v = f.select_field("northward_wind")
print(v)
Field: northward_wind (ncvar%v)
-------------------------------
Data : northward_wind(long_name=time(3), long_name=expver(2), long_name=latitude(721), long_name=longitude(1440)) m s**-1
Dimension coords: long_name=time(3) = [2023-01-01 00:00:00, 2023-02-01 00:00:00, 2023-03-01 00:00:00] gregorian
: long_name=expver(2) = [1, 5]
: long_name=latitude(721) = [90.0, ..., -90.0] degrees_north
: long_name=longitude(1440) = [0.0, ..., 359.75] degrees_east
Create a date-time object for the required time period:
5. The relative vorticity is calculated using cf.curl_xy and
plotted using cfplot.con.
The with cf.relaxed_identities(True) context manager statement prevents
the curl opereration broadcasting across the two expver dimensions because
it can’t be certain that they are the same as they lack the standardised
metadata. Setting
cf.relaxed_identities(True) allows the long_name to be treated
as standardised metadata. Since the horizontal coordinates are latitude and
longitude, the
cf.curl_xy
function automatically accounts for the Earth’s spherical geometry when
calculating the spatial derivatives in the horizontal directions, and for this
it requires the Earth’s radius. In this case the radius is not stored in the
wind fields, so must be provided by setting radius="earth" keyword
parameter. While plotting, the relative vorticity is subspaced for January
2023 and one of the experiment versions using the dictionary unpacking
operator (**) as there is an equal to sign in the identifier
("long_name=expver"):
with cf.relaxed_identities(True):
rv = cf.curl_xy(u, v, radius="earth")
cfp.con(
rv.subspace(T=jan_2023, **{"long_name=expver": 1}),
lines=False,
title="Relative Vorticity",
)
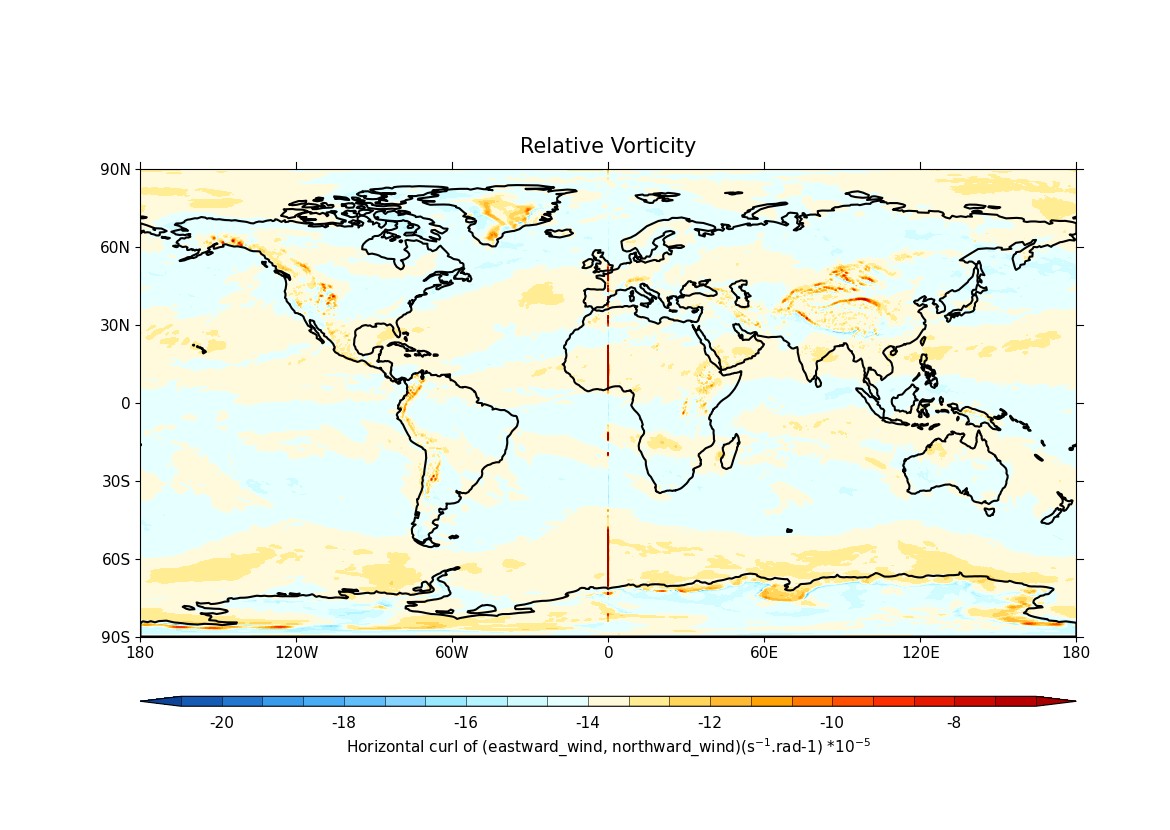
6. Although the X axis is cyclic, it is not recognised as such, owing to the
fact that the longitude coordinate bounds are missing. This results in
discontinuities in the calculated vorticity field on the plot at the
wrap-around location of 0 degrees east. The cyclicity could either be set on
the field itself or just in the curl command by setting 'x_wrap=True'
while calculating the relative vorticity. Setting rv.units = "s-1",
ensures that the units of the relative vorticity field are consistent with
the calculation and the physical interpretation of the quantity:
print(v.coordinate("X").has_bounds())
False
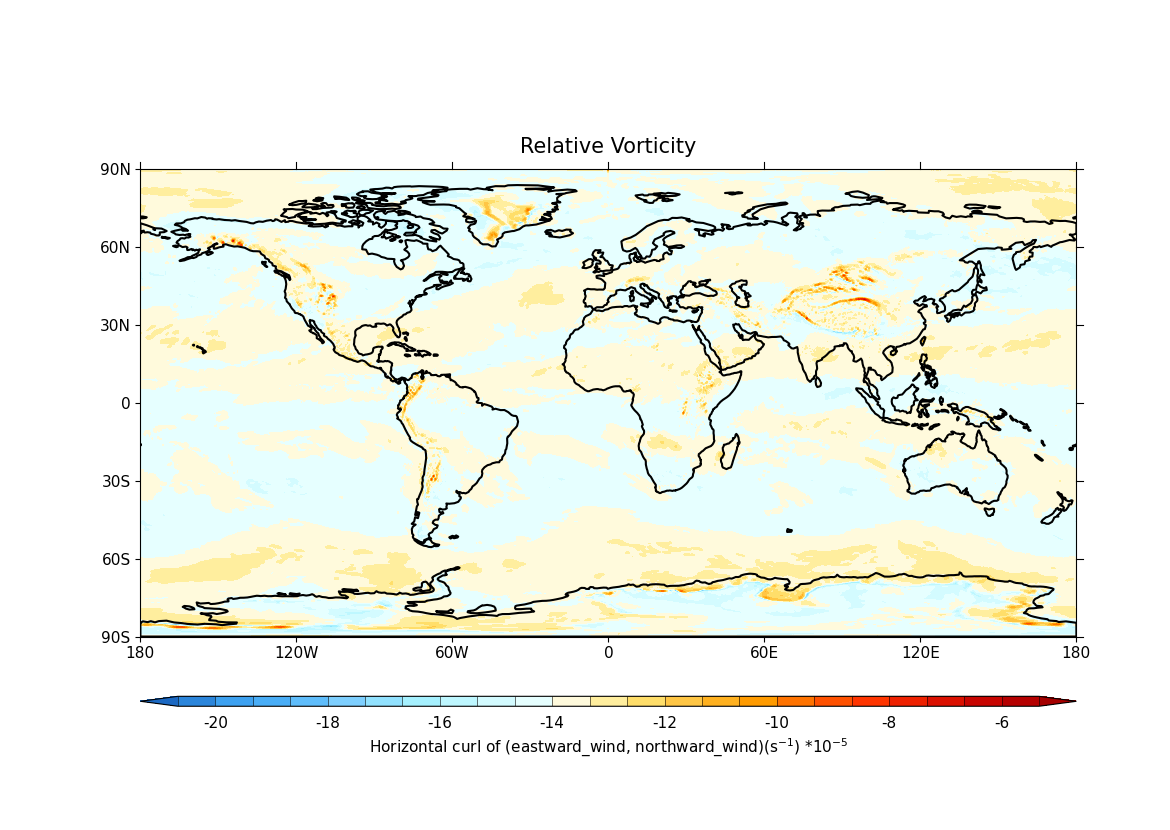
with cf.relaxed_identities(True):
rv = cf.curl_xy(u, v, x_wrap=True, radius="earth")
rv.units = "s-1"
print(rv)
Field: long_name=Horizontal curl of (eastward_wind, northward_wind) (ncvar%u)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Data : long_name=Horizontal curl of (eastward_wind, northward_wind)(long_name=time(3), long_name=expver(2), latitude(721), longitude(1440)) s-1
Dimension coords: long_name=time(3) = [2023-01-01 00:00:00, 2023-02-01 00:00:00, 2023-03-01 00:00:00] gregorian
: long_name=expver(2) = [1, 5]
: latitude(721) = [90.0, ..., -90.0] degrees_north
: longitude(1440) = [0.0, ..., 359.75] degrees_east
cfp.con(
rv.subspace(T=jan_2023, **{"long_name=expver": 1}),
lines=False,
title="Relative Vorticity",
)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 6.290 seconds)